What is Cloud Computing, What Are Its Types, and What Are Its Benefits?
Cloud Computing Definition:
Cloud computing is a way to access information and applications online, not to create, manage and maintain them on a hard drive or server. It is fast, efficient and secure. Simply put, cloud computing is the delivery of computer services. It includes servers, storage, databases, networks, software, analytics and information – over the Internet (the “cloud”) for faster innovation, flexible resources and scalable savings. In total, you only pay for the cloud services you use. It helps you reduce your operating costs, manage your infrastructure more efficiently and grow as your company’s needs change.

Computer models have been constantly evolving since Enterprise IT was founded. From large computers to virtual servers to host systems, companies are looking for ways to increase the performance and profitability of their IT architecture. Cloud computing is the next step in development. Although it shares some similarities with previous models, it has some unique features that open up new possibilities.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
As technologies become more and more integrated into the business, new needs for technology management arise. There is a greater change in operating costs, such as capital costs, or a greater desire to reduce overheads and operational complexity. Cloud computing helps achieve these goals, and for many companies, moving to the cloud is simply the best infrastructure.
- Suitability: Cloud computing makes it quick and easy to store, retrieve and share information.
- Flexibility: When information flows through places and facilities, employees can safely work anywhere. As a result, they are more productive, cooperative and happier in their work.
- Replacement: At the heart of cloud computing is the idea of ”more space”. This means that several users share the same computer resources with their cloud provider. It’s like an apartment building:
- Accounting: Cloud computing is useful in accounting because it allows the IT infrastructure to be classified as operational rather than capital expenditure. This is usually better for the health of the business as operating costs are deductible and affordable.
- Reliability: Outstanding service providers are constantly improving their architecture to ensure the highest standards of performance and availability. At the same time, third parties hosting their hosting services constantly download and update them and offer easy access to customer support.
- Scalability: Emergency service providers usually allow users to increase or decrease computer resources as needed. This means that cloud computing can rise or fall with your business. You can add or subtract bandwidth, users and services and add even more providers.
Types of Cloud Computing Deployment Model
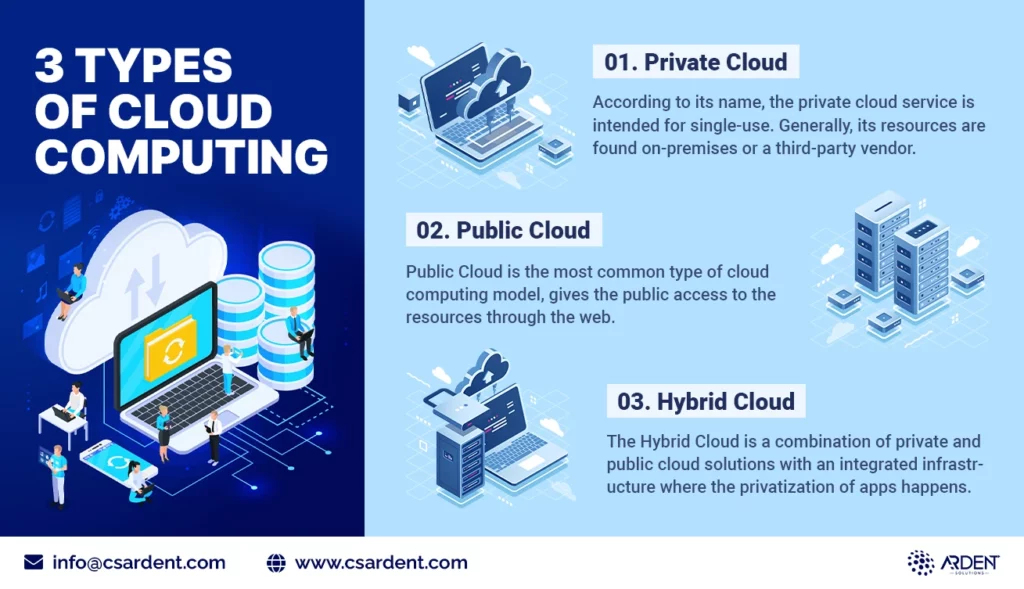
There are three main types of cloud deployment models: private, public, and hybrid. The choice of the desired model depends on the specific requirements.
- Public Cloud
Public clouds are owned and operated by external cloud service providers. They provide their own computing resources such as servers and online storage. A public cloud, such as Microsoft Azure, is an example. The cloud service provider owns and manages all of the hardware, software, and supporting infrastructure in a public cloud. You can access and control these services through a web browser.
- Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to the cloud computing resources used by a business or organisation. The private cloud can be physically located in the company’s data centre. Some companies even pay third-party service providers for their cloud hosting. A private cloud is a cloud in which services and infrastructure are hosted on a private network.
- Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds that are linked together by data and application sharing technologies. By moving data and applications between the private and public clouds, a hybrid cloud gives your business more flexibility, more deployment options, and helps you improve your existing infrastructure, security, and compliance.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
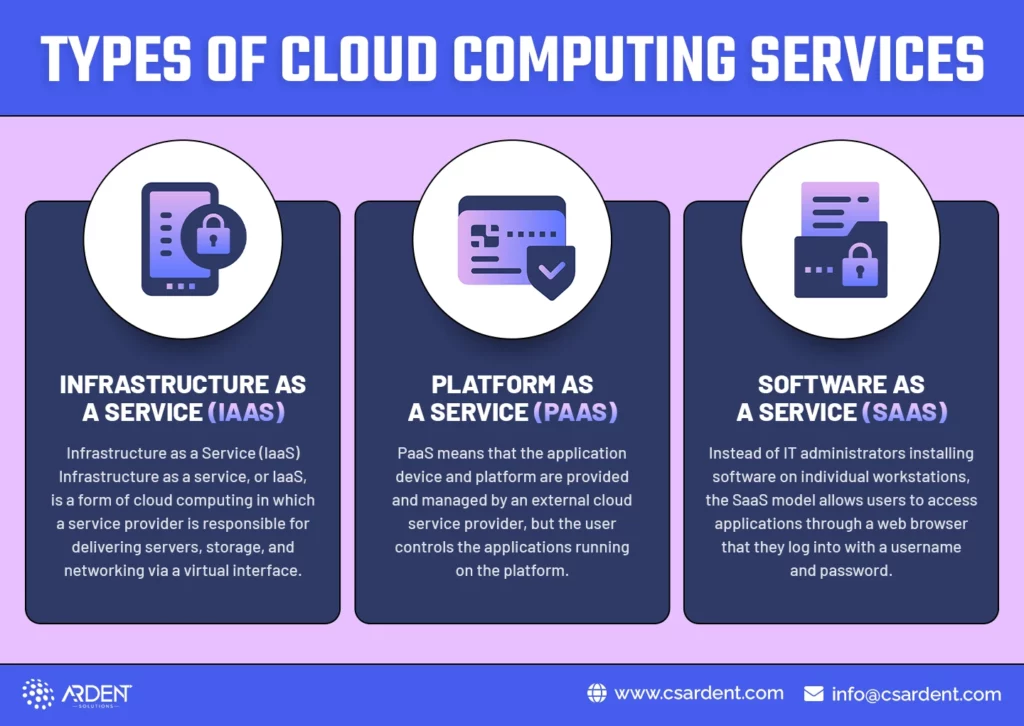
Depending on the service model, the cloud can be divided into IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). Let’s take a look at all of them.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Infrastructure as a service, or IaaS, is a form of cloud computing in which a service provider is responsible for delivering servers, storage, and networking via a virtual interface. With this service, the user does not need to manage the cloud infrastructure, but manages the storage, operating systems and applications for deployment.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS means that the application device and platform are provided and managed by an external cloud service provider, but the user controls the applications running on the platform and the data on which the application depends. First, PaaS provides users with a shared cloud platform for building and managing applications (a key component of DevOps) without the need to build and maintain a process-based infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
In this model, SaaS vendors host the software on their servers and provide it to organizations on a subscription basis. Instead of IT administrators installing software on individual workstations, the SaaS model allows users to access applications through a web browser that they log into with a username and password.
In the SaaS model, organizations can rent productivity software such as email, collaboration, and calendars. They may also use other business applications, including enterprise resource planning (ERP), document management, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Startups can use SaaS to quickly launch enterprise applications when they don’t have time to set up a server or software. Common SaaS Case Studies & examples include Dropbox, Google GSuite (applications), Cisco Webex, and GoToMeeting.
How can CS Ardent Help you Manage Apps and Microservices in Cloud Computing?
CS Ardent is a reputable provider of CloudApps and MicroService management services and offers its services in several US cities including Boston, Chicago, California, New Jersey, New York, Florida and Texas.






